By the end of this lab, you will be able to:
If you wish to follow along with the instructional videos, download and extract the zip file containing images and a text file.
The requirements for your photo gallery assignment will vary from professor to professor, but try to shoot the best image possible to help limit the amount of post processing you will need to do. As always, look over the assignment requirements and ask your instructor questions if necessary.
When working with images and video, understanding the difference between aspect ratio and resolution is important as is how they are related and intertwined. Follow along as the video discusses aspect ratio and resolution and gives examples of when they may be an issue with your work. You can find the files used in the Photoshop lab videos at the top of this lab in the section titled *downloadable files*
Put your knowledge of aspect ratios and resolution to work. This video will first demonstrate how to crop and resize without worrying about aspect ratios and then demonstrate how to crop to a specific aspect ratio before resizing the image. You can find the files used in the Photoshop lab videos at the top of this lab in the section titled *downloadable files*
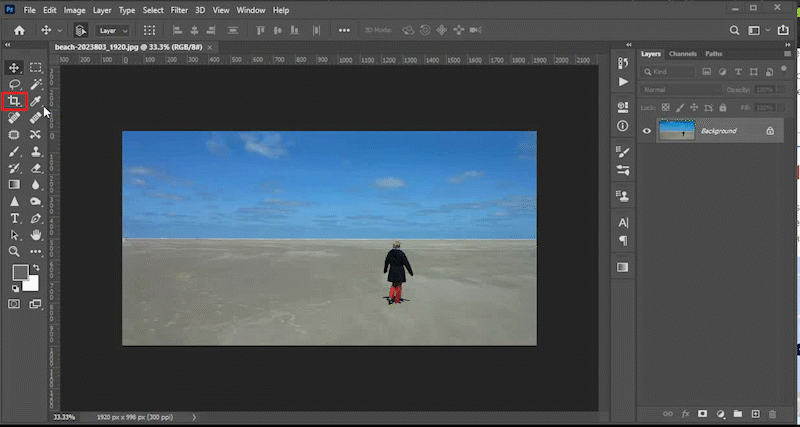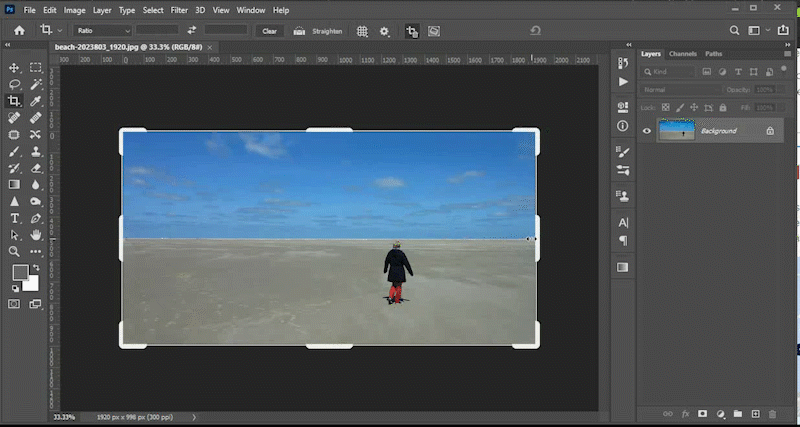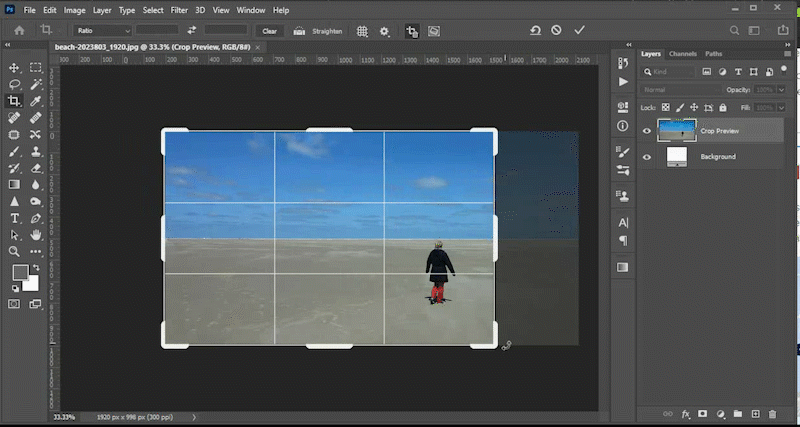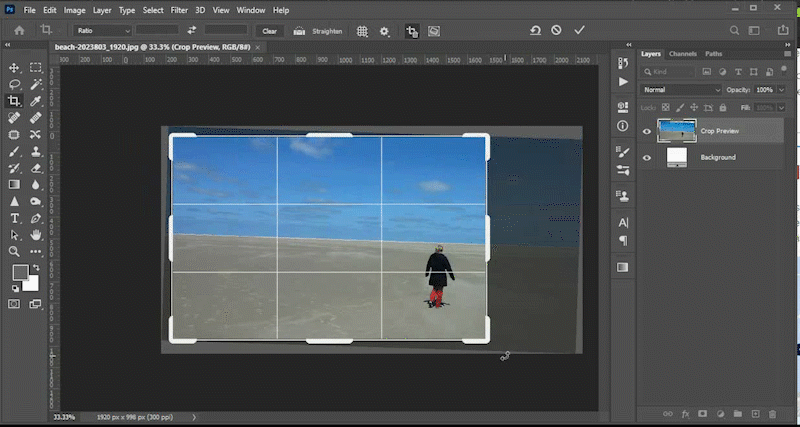
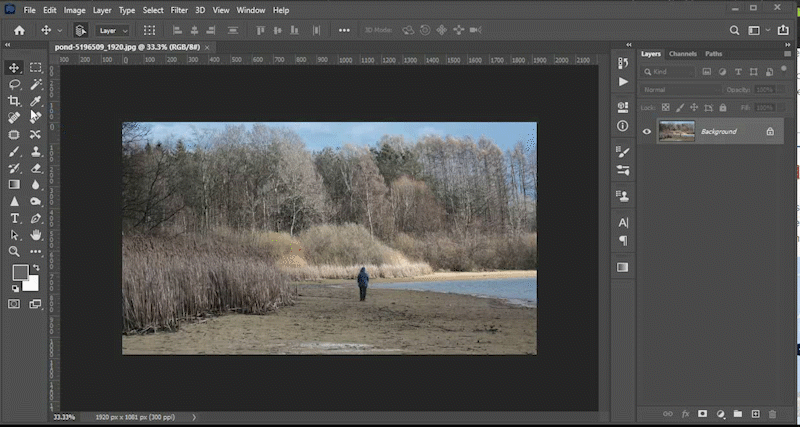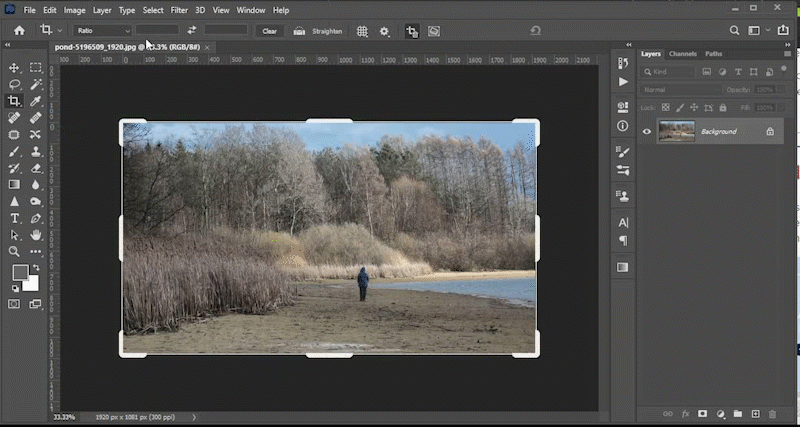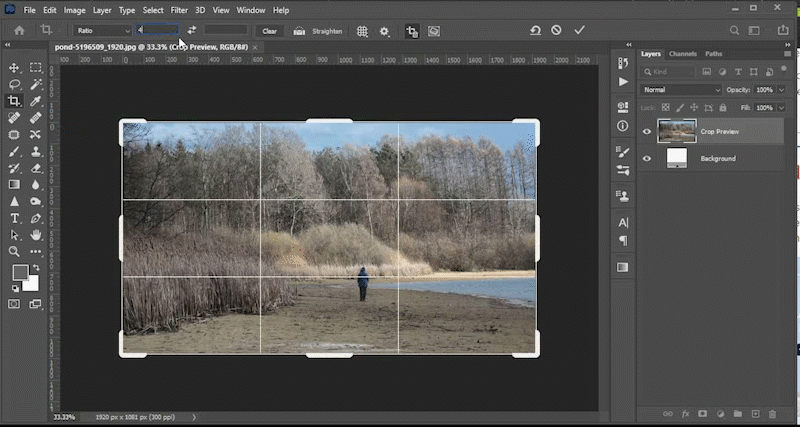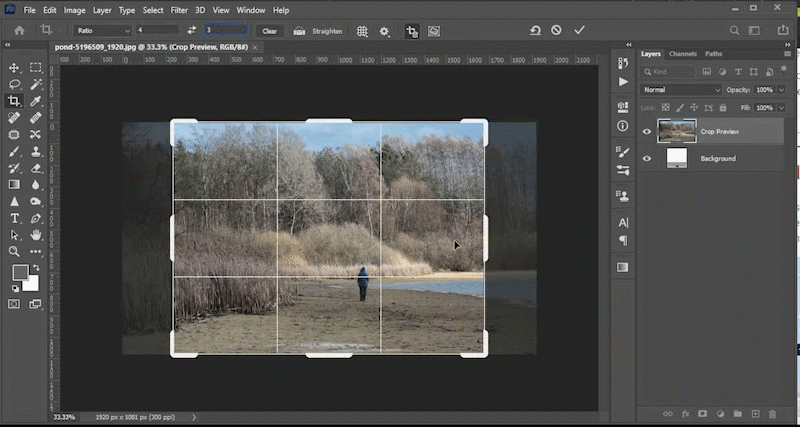
No matter how well you plan, your image may have objects that need to be hidden, moved, or replaced. This video will demonstrate how to use tools like the content aware fill tool, the patch tool, the content aware move tool, and the clone stamp tool to meet those goals. You can find the files used in the Photoshop lab videos at the top of this lab in the section titled *downloadable files*
While there are many filters in Photoshop that can help make your image look its best, this video focuses on the camera raw filter and the blur filter. You can find the files used in the Photoshop lab videos at the top of this lab in the section titled *downloadable files*
Working non-destructively in Photoshop is a great idea. You never know when you will change your mind about an edit. Adjustment layers can change the tones and colors of your image, but since they are non-destructive, they do not permantly change your pixels and can be quickly turned on and off based on your current preference. Although there are 19 adjustment layers in Photoshop, this video will focus on the black and white adjustment layer and the vibrance adjustment layer. You can find the files used in the Photoshop lab videos at the top of this lab in the section titled *downloadable files*
You can build a photo gallery two ways in Adobe Portfolio. The quick and easy way is to use the photo grid module when you create a new page in your work collection. However, your instructor may want you to place each image up one at a time using the image module. Using the image module gives you more control and forces you to think about aspect ration and resolution, so it is likely this is the technique you will be required to use for your assignment. Be sure to ask your instructor if you are unsure of the requirements.
This video will show both techniques and will take the time to remind you about some of the more important features of Photoshop while doing so. The video starts by looking at a professional looking gallery and then attempts to recreate that gallery using the tools found in Portfolio. You can find the files used in the Photoshop lab videos at the top of this lab in the section titled *downloadable files*